
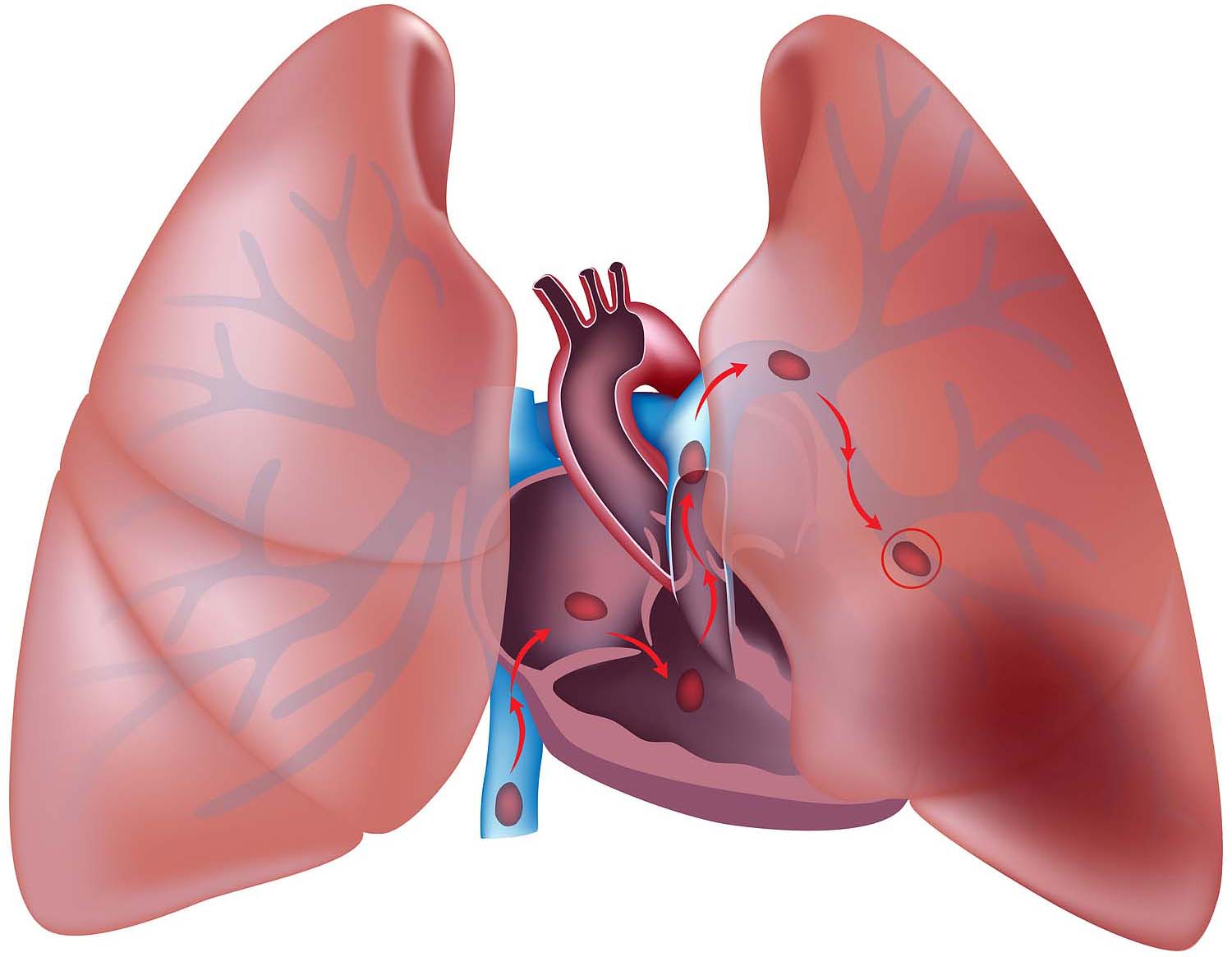
In cases that require prolonged cardiopulmonary resuscitation or, after arrest, severe ventricular dysfunction refractory to medical management, consideration for venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation should be given.īlood product cardiac arrest coagulation cryoprecipitate dobutamine norepinephrine platelet right ventricular failure.Ĭopyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. Dr Akif The four most common embolism seen in the critical care patient population are air embolism, fat embolism, cholesterol embolism, and blood embolism (clots). Our understanding of risk factors, diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis is hampered by a lack of uniform clinical case definition neither histologic nor laboratory. Amniotic fluid embolism-related coagulopathy should be managed with hemostatic resuscitation with the use of a 1:1:1 ratio of packed red cells, fresh frozen plasma, and platelets (with cryoprecipitate as needed to maintain a serum fibrinogen of >150-200 mg/dL). Amniotic fluid embolism is a leading cause of maternal mortality in developed countries. Blood pressure support with vasopressors is preferred over fluid infusion in the setting of severe right ventricular compromise. If such failure is identified, treatment that is tailored at improving right ventricular performance should be initiated with the use of inotropic agents and pulmonary vasodilators.

Where available, we recommend performing transthoracic or transesophageal echocardiography as soon as possible because this is an easy and reliable method of identifying a failing right ventricle. We describe key features of initial treatment of patients with amniotic fluid embolism. Because amniotic fluid embolism usually is seen with cardiac arrest, the initial immediate response should be to provide high-quality cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Amniotic fluid embolism is an uncommon, but potentially lethal, complication of pregnancy.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
